GYNAECOGRAPHY : INTRODUCTION, INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
INTRODUCTION
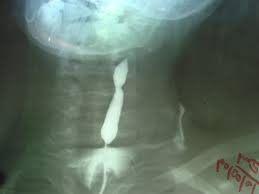
Gynaecography a term introduced by Stein involves the visualization of the uterus, tubes and ovaries by means of pneumoperitoneum plus Hysterosalpingography.
Pneumoperitoneum is gas or air trapped within the peritoneal cavity, but outside the lumen of the bowel. It is due to insufflations of gas (Carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide) during examination of organs inside the abdomen. While Hysterosalpingography is an x-ray examination of a woman’s uterus and fallopian tubes that uses special form of x-ray and contrast media.
Gynaecography technique permits an accurate diagnosis of obscure pelvic pathology and has been utilized successfully in many thousands of patients during the past twenty - five years by Dr. Stein and his group.
Gynaecography or pelvic pneumography is comprehensively defined as the term used for radiographic demonstration of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and uterine supporting ligaments by insufflations of gas (negative contrast) into the peritoneal cavity.
Gynaecography is accepted as meaning gas – contrast, pelvic organ examination. This procedure outlines the uterus and ovaries in the centre of the gas filled peritoneal cavity.
INDICATIONS
Gynaecography is indicated in female patients of any age in whom accurate assessment of the size of the uterus and ovaries is required and particularly when accurate bimanual examination is impossible such as in infants and children, in virginal and obese women, in patients with narrow introitus or patients who are so tense that examination is unsatisfactory.
1: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS):
it is a common hormonal endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. It is a condition in which a woman’s level of the sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone are out of balance. PCOS IS ALSO KNOWN AS Stein-Leventhal Syndrome or Polycystic Ovarian disease.
Symptoms of PCOS
1: pelvic pain
2: enlargement of the clitoris
3: infertility
2: Endometriosis:
is a medical condition that occurs when the linings of the uterus, called the endometrium, grows in other places, such as fallopian tubes, ovaries, or along the pelvis. When the tissue lining the inside of the uterus grows outside the uterus
Symptoms of Endometriosis
It can cause;
Chronic pains
Internal bleeding
Infertility
Fatigue and
Bowel or urinary problems.
3: Virilism:
it is a female disorder in which there is a development of secondary male sexual characteristics as a hirsutism (being hairy) and lowered voice (bass) caused by various conditions affecting hormonal regulation.
4: Amenorrhoea: is the condition when menstrual cycle does not occur in women. It is of two types, primary and secondary.
Primary Amenorrhoea: is the failure of menses to occur by age of sixteen years in the presence of normal growth and secondary sexual characteristics.
Primary symptoms include:
Congenital absence of the uterus
Failure of the ovary to receive or maintain egg cells.
Secondary Amenorrhoea: is defined as the cessation of menses sometime after menarche has occurred.
Secondary symptoms include:
Hormonal disturbances from the hypothalamus and
Pituitary gland from pre mature menopause or intrauterine scar formation.
5: Sexual precocity: Is the appearance of sexual characteristics of a matured woman before puberty. It can be classified as either Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)-dependent or GnRH-independent.
The symptoms include:
Height velocity increases
Somatic development and
Skeletal maturation which may have profound physical and psychological implications.
6: Ovarian cyst:
it an accumulation of fluid within an ovary that is surrounded by a very thin wall. Any ovarian follicle that is larger than approximately 2cm is an ovarian cyst. Ovarian cyst can range widely in size: from been as small as a pea to larger than an orange – in rare cases, ovarian cysts can become so large that the woman looks pregnant.
The symptoms include:
a. Irregular menstruation period may become painful, heavier or lighter than normal.
b. A pain in the pelvis and
c. Pressure on the bowels.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
1: Acute intraperitoneal haemorrhage: This with hypotension may be accompanied by relatively normal pulse rate instead of tachycardia produced by blood loss.
Symptoms include;
Pulse rate less than 80 per min thereby initially confusing the diagnosis of internal bleeding.
2: Acute pelvic sepsis:
it can also be referred as pelvic inflammatory diseases. It is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptom.
Signs and symptoms (when present may) Include;
a. Lower abdominal pain
b. Vaginal discharge
c. Fever
d. Burning with urination
e. Pain with sex, or irregular menstruation.
It is one of the most frequent causes of morbidity in previously healthy young women.
3. Shock: Pneumoperitoneum is contraindicated in shock, regardless of cause.
4. The transuterine route for Gynaecography is contraindicated in:
Cervicitis
Suspected pregnancy
Uterine bleeding
Tubal obstruction and
Intact hymen.



Comments
Post a Comment